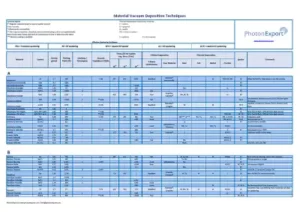
| A |
| Aluminum |
Al |
2.7 |
660 |
– |
1.08 |
677 |
821 |
1010 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Intermetallic” |
– |
– |
W |
TiB2-BN, BN |
DC |
“Alloys W/Mo/Ta. Flash evap or use BN crucible.” |
| Aluminum Antimonide |
AlSb |
4.3 |
1080 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Aluminum Arsenide |
AlAs |
3.7 |
1600 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Aluminum Bromide |
AlBr3 |
2.64 |
97 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈50 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
GR |
– |
– |
| Aluminum Carbide |
Al4C3 |
2.36/td> |
≈1400 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
≈800 |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Aluminum Fluoride |
AlF3 |
2.88 |
1291 |
S |
– |
410 |
490 |
700 |
Poor |
“Graphite, Fabmate®” |
“Mo, W, Ta” |
– |
– |
Gr |
RF |
– |
| Aluminum Nitride |
AlN |
3.26 |
>2200 |
S |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1750 |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF-R |
“Decomposes. Reactive evap in 10-3 T N2 with glow discharge.” |
| Aluminum Oxide |
Al2O3 |
3.97 |
2072 |
– |
0.336 |
– |
– |
1550 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Tungsten” |
W |
– |
W |
– |
RF-R |
“Sapphire excellent in E-beam; forms smooth, hard films.” |
| Aluminum Phosphide |
AlP |
2.42 |
2 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Aluminum, 1% Copper |
Al/Cu 99/1 wt% |
2.82 |
640 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Wire feed & flash. Difficult from dual sources.” |
| Aluminum, 1% Silicon |
“Al/Si 99/1 wt %” |
2.69 |
640 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
1010 |
– |
– |
– |
|
|
TiB2-BN |
“RF, DC” |
“Wire feed & flash. Difficult from dual sources.” |
| Antimony |
Sb |
6.68 |
630 |
S |
0.768 |
279 |
345 |
425 |
Poor |
– |
“Mo*** Ta***” |
“Mo, Ta” |
“Mo, Ta” |
“BN, C, Al2O3” |
“RF, DC” |
Evaporates well. |
| Antimony Oxide |
Sb2O3 |
5.2 |
656 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈300 |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“BN, Al2O3” |
RF-R |
Decomposes on W. |
| Antimony Selenide |
Sb2Se3 |
– |
611 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
C |
RF |
“Stoichiometry variable.” |
| Antimony Sulfide |
Sb2S3 |
4.64 |
550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈200 |
Good |
“Molybdenum, Tantalum” |
“Mo, Ta” |
– |
“Mo, Ta” |
Al2O3 |
– |
“No decomposition.” |
| Antimony Telluride |
Sb2Te3 |
6.5 |
629 |
– |
**1.00 |
|
|
600 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
C |
RF |
“Decomposes over 750°C.” |
| Arsenic |
As |
5.73 |
817 |
S |
– |
107 |
150 |
210 |
Poor |
Fabmate® |
C |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
– |
“Sublimes rapidly at low temp.” |
| Arsenic Oxide |
As2O3 |
3.74 |
312 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Arsenic Selenide |
As2Se3 |
4.75 |
~360 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Al2O3, Q” |
RF |
– |
| Arsenic Sulfide |
As2S3 |
3.43 |
300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈400 |
Fair |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
“Al2O3, Q” |
RF |
– |
| Arsenic Telluride |
As2Te3 |
6.5 |
362 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Flash |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“See JVST. 1973, 10:748” |
| B |
| Barium |
Ba |
3.51 |
725 |
– |
2.1 |
545 |
627 |
735 |
Fair |
– |
“W, Ta, Mo” |
W |
W |
Metals |
RF |
“Wets without alloying, reacts with ceramics.” |
| Barium Chloride |
BaCl2 |
3.92 |
963 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈650 |
– |
– |
“Ta, Mo” |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Barium Fluoride |
BaF2 |
4.89 |
0.355 |
S |
0.793 |
– |
– |
≈700 |
Good |
Molybdenum |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
|
| Barium Oxide |
BaO |
5.72 |
1918 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1300 |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Decomposes slightly.” |
| Barium Sulfide |
BaS |
4.25 |
1200 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1.1 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Barium Titanate |
BaTiO3 |
6.02 |
1625 |
D |
0.464 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Gives Ba. Co-evap and Sputter OK.” |
| Beryllium |
Be |
1.85 |
1278 |
– |
– |
710 |
878 |
1 |
Excellent |
“Graphite, Fabmate®” |
“W, Ta” |
W |
W |
C |
DC |
“Wets W/Mo/Ta. Evaporates easily” |
| Beryllium Carbide |
Be2C |
1.9 |
>2100 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Beryllium Chloride |
BeO |
3.01 |
2530 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1900 |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“No decomposition from E-beam guns.” |
| Beryllium Fluoride |
BeF2 |
1.99 |
800 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈200 |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Beryllium Oxide |
BeO |
3.01 |
2530 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1900 |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“No decomposition from E-beam guns.” |
| Bismuth |
Bi |
9.8 |
271 |
– |
0.79 |
330 |
410 |
520 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
“W, Mo, Ta” |
W |
W |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Resistivity high. Low Melting Point materials not ideal for sputtering.” |
| Bismuth Fluoride |
BiF3 |
5.32 |
727 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Gr |
RF |
– |
| Bismuth Oxide |
Bi2O3 |
8.55 |
860 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1400 |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Bismuth Selenide |
Bi2Se3 |
6.82 |
710 |
D |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈650 |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Gr, Q” |
RF |
“Co-evap from 2 sources or sputter.” |
| Bismuth Sulfide |
Bi2S3 |
7.39 |
685 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Bismuth Telluride |
Bi2Te3 |
7.7 |
573 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈600 |
– |
– |
“W, Mo” |
– |
– |
“Gr, Q” |
RF |
“Co-evap from 2 sources or sputter.” |
| Bismuth Titanate |
Bi2Ti2O7 |
– |
870 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Sputter or co-evap from 2 sources in 10-2 Torr O2.” |
| Boron |
B |
2.34 |
2079 |
– |
0.389 |
1.278 |
1.548 |
1797 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
C |
– |
– |
C |
RF |
“Explodes with rapid cooling. Forms carbide with container.” |
| Boron Carbide |
B4C |
2.52 |
2350 |
– |
**1.00 |
2.5 |
2.58 |
2650 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Similar to chromium.” |
| Boron Nitride |
BN |
2.25 |
3000 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
1600 |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Decomposes when sputtered. Reactive preferred.” |
| Boron Oxide |
B2O3 |
1.81 |
≈450 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1400 |
Good |
Molybdenum |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Boron Sulfide |
B2S3 |
1.55 |
310 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
800 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Gr |
RF |
– |
| C |
| Cadmium |
Cd |
8.64 |
321 |
– |
0.682 |
64 |
120 |
180 |
Poor |
– |
“W,
Mo, Ta” |
– |
“W,
Mo, Ta” |
“Al2O3,
Q” |
“DC,
RF” |
“Bad for vacuum
systems. Low sticking coefficient.” |
| Cadmium Antimonide |
Cd3Sb2 |
6.92 |
456 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Cadmium Arsenide |
Cd3As2 |
6.21 |
721 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Cadmium Bromide |
CdBr2 |
5.19 |
567 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Cadmium Chloride |
CdCl2 |
4.05 |
568 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Cadmium Fluoride |
CdF2 |
6.64 |
1.1 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Cadmium Iodide |
CdI2 |
5.67 |
387 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈250 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Cadmium Oxide |
CdO |
6.95 |
>1500 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
≈530 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RF-R |
Disproportionates. |
| Cadmium Selenide |
CdSe |
5.81 |
>1350 |
S |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
540 |
Good |
“Molybdenum,
Tantalum” |
“Mo,
Ta” |
– |
– |
“Al2O3,
Q” |
RF |
“Evaporates
easily.” |
| Cadmium Sulfide |
CdS |
4.82 |
1750 |
S |
1.02 |
– |
– |
550 |
Fair |
– |
“W,
Mo, Ta” |
– |
W |
“Al2O3,
Q” |
RF |
“Sticking
coefficient affected by substrate.” |
| Cadmium Telluride |
CdTe |
5.85 |
1092 |
– |
0.98 |
– |
– |
450 |
– |
– |
“W,
Mo, Ta” |
W |
“W,
Ta, Mo” |
– |
RF |
“Stoichiometry
depends on substrate temp. n~2.6.” |
| Calcium |
Ca |
1.54 |
839 |
S |
2.62 |
272 |
357 |
459 |
Poor |
– |
W |
W |
W |
“Al2O3,
Q” |
– |
Corrodes in air. |
| Calcium Fluoride |
CaF2 |
3.18 |
1423 |
– |
0.775 |
– |
– |
≈1100 |
– |
– |
“W, Mo, Ta” |
“W, Mo, Ta” |
“W, Mo, Ta” |
Q |
RF |
“Rate control important. Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Calcium Oxide |
CaO |
~3.3 |
2614 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1700 |
– |
– |
“W, Mo” |
– |
– |
ZrO2 |
RF-R |
“Forms volatile oxides with W/Mo.” |
| Calcium Silicate |
CaSiO3 |
2.91 |
1540 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Calcium Sulfide |
CaS |
2.5 |
2525 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
1100 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Calcium Titanate |
CaTiO3 |
4.1 |
1975 |
– |
– |
1490 |
1600 |
1690 |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Disproportionates except in sputtering.” |
| Calcium Tungstate |
CaWO4 |
6.06 |
1200 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Carbon |
C |
1.8–2.1 |
≈3652 |
S |
3.26 |
1657 |
1867 |
2137 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
PDC |
“E-beam preferred. Arc evaporation. Poor film adhesion.” |
| Cerium |
Ce |
~6.70 |
798 |
– |
**1.00 |
970 |
1150 |
1380 |
Good |
– |
“W, Ta” |
W |
“W, Ta” |
Al2O3 |
“DC, RF” |
– |
| Cerium (III) Oxide |
Ce2O3 |
6.86 |
1692 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Fair |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Alloys with source. Use 0.015″”–0.020″” W boat.” |
| Cerium (IV) Oxide |
CeO2 |
7.13 |
≈2600 |
– |
**1.00 |
1890 |
2000 |
2310 |
Good |
“Tantalum, Graphite, Fabmate®” |
W |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Very little decomposition.” |
| Cerium Fluoride |
CeF3 |
6.16 |
1460 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈900 |
Good |
“Tungsten, Tantalum, Molybdenum” |
“W, Mo, Ta” |
– |
“Mo, Ta” |
– |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas. n~1.7.” |
| Cesium |
Cs |
1.88 |
28 |
– |
– |
-16 |
22 |
80 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
– |
– |
| Cesium Bromide |
CsBr |
3.04 |
636 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈400 |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Cesium Chloride |
CsCl |
3.99 |
645 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Cesium Fluoride |
CsF |
4.12 |
682 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Cesium Hydroxide |
CsOH |
3.68 |
272 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Cesium Iodide |
CsI |
4.51 |
626 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Chiolite |
Na5Al3F14 |
2.9 |
735 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈800 |
– |
– |
“Mo, W” |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
|
| Chromium |
Cr |
7.2 |
1.857 |
S |
0.305 |
837 |
977 |
1157 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Graphite, Tungsten” |
“Cr Plated W Rods” |
W |
W |
VitC |
DC |
“Films very adherent. High rates possible.” |
| Chromium Boride |
CrB |
6.17 |
1950-2050 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Chromium (II) Bromide |
CrBr2 |
4.36 |
842 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Chromium Carbide |
Cr3C2 |
6.68 |
1895 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈2000 |
Fair |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Chromium Chloride |
CrCl2 |
2.88 |
824 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
550 |
– |
– |
Fe |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Chromium Oxide |
Cr2O3 |
5.21 |
2266 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈2000 |
Good |
– |
“W, Mo” |
– |
W |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Disproportionates to lower oxides; reoxidizes at 600°C in air.” |
| Chromium Silicide |
CrSi2 |
5.5 |
1490 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Chromium-Silicon Monoxide |
Cr-SiO |
– |
– |
S |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
W |
– |
W |
– |
RF |
Flash evaporate. |
| Cobalt † |
Co |
8.9 |
1495 |
– |
0.343 |
850 |
990 |
1200 |
Excellent |
“Direct in Hearth” |
“W, Nb” |
– |
W |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Alloys with W/Ta/Mo.” |
| Cobalt Bromide |
CoBr2 |
4.91 |
678 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Cobalt Chloride |
CoCl2 |
3.36 |
724 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
472 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Cobalt Oxide |
CoO |
6.45 |
1795 |
– |
0.412 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“DC-R, RF-R” |
“Sputtering preferred.” |
| Copper |
Cu |
8.92 |
1083 |
– |
0.437 |
727 |
857 |
1017 |
Excellent |
“Graphite, Molybdenum” |
Mo |
W |
W |
“Al2O3, Mo, Ta” |
DC |
“Adhesion poor. Use interlayer (Cr). Evaporates using any source material.” |
| Copper Chloride |
CuCl |
4.14 |
430 |
* |
– |
– |
– |
≈600 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Copper Oxide |
Cu2O |
6 |
1235 |
S |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈600 |
Good |
“Graphite, Fabmate®, Tantalum” |
Ta |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
“DC-R, RF-R” |
– |
| Copper Sulfide |
Cu2S |
5.6 |
1100 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Cryolite |
Na3AlF6 |
2.9 |
1 |
– |
– |
1020 |
1260 |
1480 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Tungsten” |
“W, Mo, Ta” |
– |
“W, Mo, Ta” |
VitC |
RF |
“Large chunks reduce spitting. Little decomposition.” |
| D |
| Dysprosium |
Dy |
8.55 |
1412 |
– |
0.6 |
625 |
750 |
900 |
Good |
“Direct in Hearth” |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| Dysprosium Fluoride |
DyF3 |
– |
1360 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈800 |
Good |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Dysprosium Oxide |
Dy2O3 |
7.81 |
2340 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1,400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
Loses oxygen |
| E |
| Erbium |
Er |
9.07 |
1529 |
S |
0.74 |
650 |
775 |
930 |
Good |
“Tungsten, Tantalum” |
“W, Ta” |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| Erbium Fluoride |
ErF3 |
7.82 |
1350 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈750 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“See JVST. 1985; A3(6):2320.” |
| Erbium Oxide |
Er2O3 |
8.64 |
2350 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1600 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
Loses oxygen. |
| Europium |
Eu |
5.24 |
822 |
S |
**1.00 |
280 |
360 |
480 |
Fair |
– |
“W, Ta” |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Low Ta solubility.” |
| Europium Fluoride |
EuF2 |
6.5 |
1380 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈950 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Europium Oxide |
Eu2O3 |
7.42 |
2350 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1600 |
Good |
– |
“Ta, W” |
– |
– |
ThO2 |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Loses oxygen. Films clear and hard.” |
| Europium Sulfide |
EuS |
5.75 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| G |
| Gadolinium † |
Gd |
7.9 |
1313 |
– |
0.67 |
760 |
900 |
1175 |
Excellent |
“Direct in Hearth” |
Ta |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“High Ta solubility” |
| Gadolinium Carbide |
GdC2 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
C |
RF |
“Decomposes under sputtering.” |
| Gadolinium Oxide |
Gd2O3 |
7.41 |
2330 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
Loses oxygen. |
| Gallium |
Ga |
5.9 |
30 |
– |
– |
619 |
742 |
907 |
Good |
Fabmate® |
– |
– |
– |
“Al2O3, Q” |
– |
“Alloys with W/Ta/Mo. Use E-beam gun. Low Melting Point materials not ideal for sputtering.” |
| Gallium Antimonide |
GaSb |
5.6 |
710 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Fair |
– |
“W, Ta” |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Flash evaporate. |
| Gallium Arsenide |
GaAs |
5.3 |
1238 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
“Graphite, Fabmate®” |
“W, Ta” |
– |
– |
C |
RF |
Flash evaporate. |
| Gallium Nitride |
GaN |
6.1 |
800 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈200 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Evaporate Ga in 10-3 Torr N2.” |
| Gallium Oxide |
Ga2O3 |
6.44 |
1900 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Loses oxygen. |
| Gallium Phosphide |
GaP |
4.1 |
1540 |
– |
– |
– |
770 |
920 |
– |
– |
“W, Ta” |
– |
W |
Q |
RF |
“Does not decompose. Rate control important.” |
| Germanium |
Ge |
5.35 |
937 |
– |
0.516 |
812 |
957 |
1167 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
“W, C, Ta” |
– |
– |
“Q, Al2O3” |
DC |
“Excellent films from E-beam.” |
| Germanium (II) Oxide |
GeO |
– |
700 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Germanium (III) Oxide |
GeO2 |
6.24 |
1086 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈625 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Tantalum, Molybdenum” |
“Ta, Mo” |
– |
“W, Mo” |
“Q, Al2O3” |
RF-R |
“Similar to SiO; film predominantly GeO.” |
| Germanium Nitride |
Ge3N2 |
5.2 |
450 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
~650 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF-R |
“Sputtering preferred.” |
| Germanium Telluride |
GeTe |
6.2 |
725 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
381 |
– |
– |
“W, Mo” |
– |
W |
“Q, Al2O3” |
RF |
– |
| Glass, Schott® 8329 |
— |
2.2 |
1.3 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Excellent |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Evaporable alkali glass. Melt in air before evaporating.” |
| Gold |
Au |
19.32 |
1064 |
– |
0.381 |
807 |
947 |
1132 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Tungsten” |
“W*** Mo***” |
– |
– |
“Al2O3, BN” |
DC |
“Films soft; not very adherent.” |
| H |
| Hafnium |
Hf |
13.31 |
2227 |
– |
0.36 |
2160 |
2250 |
3090 |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| Hafnium Boride |
HfB2 |
10.5 |
3250 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“DC, RF” |
– |
| Hafnium Carbide |
HfC |
12.2 |
≈3890 |
S |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈2600 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Hafnium Nitride |
HfN |
13.8 |
3305 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Hafnium Oxide |
HfO2 |
9.68 |
2758 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈2500 |
Fair |
“Direct in Hearth” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
Film HfO. |
| Hafnium Silicide |
HfSi2 |
7.2 |
1750 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Holmium |
Ho |
8.8 |
1474 |
– |
0.58 |
650 |
770 |
950 |
Good |
– |
“W, Ta” |
W |
W |
– |
– |
– |
| Holmium Fluoride |
HoF3 |
7.68 |
1143 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈800 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
“DC, RF” |
– |
| Holmium Oxide |
Ho2O3 |
8.41 |
2370 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
Loses oxygen. |
| I |
| Inconel® |
Ni/Cr/Fe |
8.5 |
1425 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Tungsten” |
W |
W |
W |
– |
DC |
“Use fine wire wrapped on W. Low rate required for smooth films.” |
| Indium |
In |
7.3 |
157 |
– |
0.841 |
487 |
597 |
742 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite, Molybdenum” |
“W, Mo” |
– |
W |
“Gr, Al2O3” |
DC |
“Wets W and Cu. Use Mo liner. Low Melting Point materials not ideal for sputtering.” |
| Indium (I) Oxide |
In2O |
6.99 |
≈600 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
650 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Decomposes under sputtering.” |
| Indium (III) Oxide |
In2O3 |
7.18 |
850 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1200 |
Good |
– |
“W, Pt” |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
– |
– |
| Indium (I) Sulfide |
In2S |
5.87 |
653 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
650 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Gr |
RF |
– |
| Indium (II) Sulfide |
InS |
5.18 |
692 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
650 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Gr |
RF |
– |
| Indium (III) Sulfide |
In2S3 |
4.9 |
1050 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
850 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Gr |
RF |
Film In2S. |
| Indium (II) Telluride |
InTe |
6.29 |
696 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Indium (III) Telluride |
In2Te3 |
5.78 |
667 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Sputtering preferred; or co-evaporate from 2 sources; flash.” |
| Indium Antimonide |
InSb |
5.8 |
535 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Decomposes. Sputtering preferred; or co-evaporate.” |
| Indium Arsenide |
InAs |
5.7 |
943 |
– |
– |
780 |
870 |
970 |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Indium Nitride |
InN |
7 |
1200 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Indium Phosphide |
InP |
4.8 |
1070 |
– |
– |
– |
630 |
730 |
– |
– |
“W, Ta” |
– |
“W, Ta” |
Gr |
RF |
“Deposits are P rich.” |
| Indium Selenide |
In2Se3 |
5.67 |
890 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Sputtering preferred; or co-evaporate from 2 sources; flash.” |
| Indium Tin Oxide |
“In2O3/SnO290/10 wt %” |
– |
1.8 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Iridium |
Ir |
22.42 |
2410 |
– |
0.129 |
1850 |
2080 |
2380 |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| Iron † |
Fe |
7.86 |
1535 |
– |
0.349 |
858 |
998 |
1180 |
Excellent |
Fabmate®‡ |
W |
W |
W |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Attacks W. Films hard, smooth. Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Iron (II) Oxide |
FeO |
5.7 |
1369 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Decomposes; sputtering preferred.” |
| Iron (III) Oxide |
Fe2O3 |
5.24 |
1565 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
W |
– |
W |
– |
– |
“Disproportionate to Fe3O4 at 1,530°C.” |
| Iron Bromide |
37288 |
4.64 |
684 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
561 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Fe |
RF |
– |
| Iron Chloride |
FeCl2 |
3.16 |
670 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Fe |
RF |
– |
| Iron Iodide |
FeI2 |
5.32 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Fe |
RF |
– |
| Iron Sulfide |
FeS |
4.74 |
1193 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
Decomposes |
| K |
| Kanthal |
FeCrAl |
7.1 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
W |
W |
– |
DC |
– |
| L |
| Lanthanum |
La |
6.15 |
921 |
– |
0.92 |
990 |
1212 |
1388 |
Excellent |
“Tungsten, Tantalum” |
“W, Ta” |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
“Films will burn in air if scraped.” |
| Lanthanum Boride |
LaB6 |
2.61 |
2210 |
D |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Lanthanum Bromide |
LaBr3 |
5.06 |
783 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
RF |
Hygroscopic. |
| Lanthanum Fluoride |
LaF3 |
~6.0 |
1490 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
900 |
Good |
“Tantalum, Molybdenum” |
“Ta, Mo” |
– |
Ta |
– |
RF |
“No decomposition. n~1.6.” |
| Lanthanum Oxide |
La2O3 |
6.51 |
2307 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
1400 |
Good |
“Graphite, Fabmate®, Tungsten” |
“W, Ta” |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Loses oxygen. n~1.73.” |
| Lead |
Pb |
11.34 |
328 |
– |
1.13 |
342 |
427 |
497 |
Excellent |
Fabmate® |
“W, Mo” |
W |
“W, Ta” |
“Al2O3, Q” |
DC |
– |
| Lead Bromide |
PbBr2 |
6.66 |
373 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Lead Chloride |
PbCl2 |
5.85 |
501 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈325 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
“Little decomposition.” |
| Lead Fluoride |
PbF2 |
8.24 |
855 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈400 |
– |
– |
“W, Mo” |
– |
– |
BeO |
RF |
– |
| Lead Iodide |
PbI2 |
6.16 |
402 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
– |
– |
| Lead Oxide |
PbO |
9.53 |
886 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Q, Al2O3” |
RF-R |
“No decomposition. n~2.6.” |
| Lead Selenide |
PbSe |
8.1 |
1065 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
“W, Mo” |
– |
W |
“Gr, Al2O3” |
RF |
– |
| Lead Stannate |
PbSnO3 |
8.1 |
1115 |
– |
– |
670 |
780 |
905 |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
Disproportionates. |
| Lead Sulfide |
PbS |
7.5 |
1114 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
500 |
– |
– |
W |
– |
“W, Mo” |
“Q, Al2O3” |
RF |
“Little decomposition.” |
| Lead Telluride |
PbTe |
8.16 |
917 |
– |
0.651 |
780 |
910 |
1050 |
– |
– |
“Mo, Pt, Ta” |
– |
– |
“Al2O3, Gr” |
RF |
“Deposits are Ta rich. Sputtering preferred.” |
| Lead Titanate |
PbTiO3 |
7.52 |
– |
– |
1.16 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Lithium |
Li |
0.53 |
181 |
– |
5.9 |
227 |
307 |
407 |
Good |
Tantalum |
Ta |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
– |
“Metal reacts quickly in air.” |
| Lithium Bromide |
LiBr |
3.46 |
550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
Ni |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Lithium Chloride |
LiCl |
2.07 |
605 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
400 |
– |
– |
Ni |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Lithium Fluoride |
LiF |
2.64 |
845 |
– |
0.778 |
875 |
1020 |
1180 |
Good |
“Tantalum, Tungsten, Molybdenum” |
“Ni, Ta, Mo, W” |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
“Rate control important for optical films. Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Lithium Iodide |
LiI |
4.08 |
449 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
400 |
– |
– |
“Mo, W” |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Lithium Niobate |
LiNbO3 |
– |
– |
– |
0.463 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Lithium Oxide |
Li2O |
2.01 |
>1700 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
850 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Lutetium |
Lu |
9.84 |
1663 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1300 |
Excellent |
“Direct in Hearth” |
Ta |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
“RF, DC” |
– |
| Lutetium Oxide |
Lu2O3 |
9.42 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| M |
| Magnesium |
Mg |
1.74 |
649 |
S |
1.61 |
185 |
247 |
327 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Graphite, Tungsten” |
“W, Mo, Ta, Cb” |
W |
W |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Extremely high rates possible.” |
| Magnesium Aluminate |
MgAl2O4 |
3.6 |
2135 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Natural spinel. |
| Magnesium Bromide |
MgBr2 |
3.72 |
700 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈450 |
– |
– |
Ni |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Magnesium Chloride |
MgCl2 |
2.32 |
714 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
400 |
– |
– |
Ni |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Magnesium Fluoride |
MgF2 |
2.9–3.2 |
1261 |
– |
0.637 |
– |
– |
1 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite, Molybdenum” |
“Mo, Ta” |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
“Substrate temp and rate control important. Reacts with W. Mo OK.” |
| Magnesium Iodide |
MgI2 |
4.43 |
<637 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
200 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Magnesium Oxide |
MgO |
3.58 |
2852 |
– |
0.411 |
– |
– |
1300 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
– |
– |
– |
“C, Al2O3” |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Evaporates in 10-3Torr O2 for stoichiometry.” |
| Manganese |
Mn |
7.2 |
1244 |
S |
0.377 |
507 |
572 |
647 |
Good |
Tungsten |
“W, Ta, Mo” |
W |
W |
Al2O3 |
DC |
– |
| Manganese (II) Oxide |
MnO |
5.37 |
1945 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Manganese (III) Oxide |
Mn2O3 |
4.5 |
1080 |
– |
0.467 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Manganese (IV) Oxide |
MnO2 |
5.03 |
535 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Poor |
– |
W |
– |
W |
– |
RF-R |
“Loses oxygen at 535°C.” |
| Manganese Bromide |
MnBr2 |
4.39 |
– |
D |
– |
– |
– |
500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Manganese Chloride |
MnCl2 |
2.98 |
650 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
450 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Manganese Sulfide |
MnS |
3.99 |
– |
D |
– |
– |
– |
1300 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Mercury |
Hg |
13.55 |
≈39 |
– |
– |
-68 |
-42 |
-6 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Mercury Sulfide |
HgS |
8.1 |
584 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
250 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Molybdenum |
Mo |
10.2 |
2617 |
– |
0.257 |
1592 |
1822 |
2117 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Films smooth, hard. Careful degas required.” |
| Molybdenum Boride |
MoB2 |
7.12 |
2100 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Molybdenum Carbide |
Mo2C |
8.9 |
2687 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Evaporation of Mo(CO)6 yields Mo2C.” |
| Molybdenum Sulfide |
MoS2 |
4.8 |
1185 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈50 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Molybdenum Oxide |
MoO3 |
4.69 |
795 |
S |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈900 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
Mo |
“Al2O3, BN” |
RF |
“Slight oxygen loss.” |
| Molybdenum Silicide |
MoSi2 |
6.31 |
2050 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| N |
| Neodymium |
Nd |
7.01 |
1021 |
– |
**1.00 |
731 |
871 |
1062 |
Excellent |
Tantalum |
Ta |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Low W solubility.” |
| Neodymium Fluoride |
NdF3 |
6.5 |
1410 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈900 |
Good |
“Tungsten, Molybdenum” |
“Mo, W” |
– |
“Mo, Ta” |
Al2O3 |
RF |
“Very little decomposition.” |
| Neodymium Oxide |
Nd2O3 |
7.24 |
≈1900 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1400 |
Good |
“Tantalum, Tungsten” |
“Ta, W” |
– |
– |
ThO2 |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Loses oxygen; films clear. E-beam preferred.” |
| Nichrome IV® † |
Ni/Cr |
8.5 |
1395 |
– |
**1.00 |
847 |
987 |
1217 |
Excellent |
Fabmate® |
Mo***, W***, Ta*** |
W |
W, Ta |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Alloys with W/Ta/Mo.” |
| Nickel † |
Ni |
8.9 |
1453 |
– |
0.331 |
927 |
1072 |
1262 |
Excellent |
Fabmate®‡ |
W*** |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Alloys with W/Ta/Mo. Smooth adherent films.” |
| Nickel Bromide |
NiBr2 |
5.1 |
963 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
362 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Nickel Chloride |
NiCl2 |
3.55 |
1001 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
444 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Nickel Oxide |
NiO |
6.67 |
1984 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1470 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF-R |
“Dissociates on heating.” |
| Nickel/Iron † |
Ni/Fe |
– |
– |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Fabmate®‡, |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Nimendium † |
Ni3%Mn |
8.8 |
1425 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| Niobium |
Nb |
8.57 |
2468 |
– |
0.492 |
1728 |
1977 |
2287 |
Excellent |
Fabmate® |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Attacks W source.” |
| Niobium (II) Oxide |
NbO |
7.3 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1100 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Niobium (III) Oxide |
Nb2O3 |
7.5 |
1780 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
W |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Niobium (V) Oxide |
Nb2O5 |
4.47 |
1485 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
W |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Niobium Boride |
NbB2 |
6.97 |
2900 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Niobium Carbide |
NbC |
7.6 |
3500 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Niobium Nitride |
NbN |
8.4 |
2573 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Reactive. Evaporates Nb in 10-3 Torr N2.” |
| Niobium Telluride |
NbTe2 |
7.6 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Composition variable.” |
| Niobium-Tin |
Nb3Sn |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Excellent |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Co-evaporate from 2 sources.” |
| O |
| Osmium |
Os |
22.48 |
3045 |
– |
– |
2170 |
2430 |
2760 |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| Osmium Oxide |
Os2O3 |
– |
– |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Deposits Os in 10-3Torr O2.” |
| P |
| Palladium |
Pd |
12.02 |
1554 |
S |
0.357 |
842 |
992 |
1192 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite, Tungsten” |
W*** |
W |
W |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Alloys with refractory metals.” |
| Palladium Oxide |
PdO |
9.7 |
870 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
575 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF-R |
Decomposes. |
| Parylene |
C8H8 |
1.1 |
300–400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Vapor-depositable plastic.” |
| Permalloy® † |
Ni/Fe/Mo/Mn |
8.7 |
1395 |
– |
**1.00 |
947 |
1047 |
1307 |
Good |
Fabmate®‡ |
W |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
DC |
Film low in Ni. |
| Phosphorus |
P |
1.82 |
44.1 |
– |
– |
327 |
361 |
402 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
– |
“Material reacts violently in air.” |
| Phosphorus Nitride |
P3N5 |
2.51 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Platinum |
Pt |
21.45 |
1772 |
|
0.245 |
1292 |
1492 |
1747 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
W |
W |
W |
C |
DC |
“Alloys with metals. Films soft, poor adhesion.” |
| Platinum Oxide |
PtO2 |
10.2 |
450 |
– |
– |
-7 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF-R |
“E-beam preferred for evaporation.” |
| Plutonium |
Pu |
19.84 |
641 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Polonium |
Po |
9.4 |
254 |
– |
– |
117 |
170 |
244 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
– |
– |
| Potassium |
K |
0.86 |
63 |
– |
– |
23 |
60 |
125 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
Q |
|
“Metal reacts rapidly in air. Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Potassium Bromide |
KBr |
2.75 |
734 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈450 |
– |
– |
“Ta, Mo” |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Potassium Chloride |
KCl |
1.98 |
770 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
510 |
Good |
Tantalum |
“Ta, Ni” |
|
|
|
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Potassium Fluoride |
KF |
2.48 |
858 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Potassium Hydroxide |
KOH |
2.04 |
360 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Potassium Iodide |
KI |
3.13 |
681 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Praseodymium |
Pr |
6.77 |
931 |
– |
**1.00 |
800 |
950 |
1150 |
Good |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| Praseodymium Oxide |
Pr2O3 |
7.07 |
– |
D |
– |
– |
– |
1400 |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
ThO2 |
“RF, RF-R” |
Loses oxygen. |
| PTFE |
PTFE |
2.9 |
330 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Baffled source. Film structure doubtful.” |
| R |
| Radium |
Ra |
“5 (?)” |
700 |
– |
– |
246 |
320 |
416 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Rhenium |
Re |
20.53 |
3180 |
– |
0.15 |
1928 |
2207 |
2571 |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| Rhenium Oxide |
ReO3 |
~7 |
– |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Evaporate Re in 10-3 Torr O2.” |
| Rhodium |
Rh |
12.4 |
1966 |
– |
0.21 |
1277 |
1472 |
1707 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Tungsten” |
W |
W |
W |
“ThO2, VitC” |
DC |
“E-beam gun preferred.” |
| Rubidium |
Rb |
1.48 |
39 |
– |
– |
-3 |
37 |
111 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
– |
– |
| Rubidium Chloride |
RbCl |
2.09 |
718 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Rubidium Iodide |
RbI |
3.55 |
647 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Ruthenium |
Ru |
12.3 |
2310 |
– |
0.182 |
1780 |
1990 |
2260 |
Poor |
|
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
– |
| S |
| Samarium |
Sm |
7.52 |
1074 |
– |
0.89 |
373 |
460 |
573 |
Good |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
DC |
— |
| Samarium Oxide |
Sm2O3 |
8.35 |
2350 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
ThO2 |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Loses oxygen. Films smooth, clear.” |
| Samarium Sulfide |
Sm2S3 |
5.73 |
1900 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Scandium |
Sc |
2.99 |
1541 |
– |
0.91 |
714 |
837 |
1002 |
Excellent |
“Tungsten, Molybdenum” |
W |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
Alloys with Ta. |
| Scandium Oxide |
Sc2O3 |
3.86 |
2300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
~400 |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Selenium |
Se |
4.81 |
217 |
– |
0.864 |
89 |
125 |
170 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Tungsten, Molybdenum” |
“W, Mo” |
“W, Mo” |
“W, Mo” |
Al2O3 |
– |
“Bad for vacuum systems. High V.P. Low Melting Point materials not ideal for sputtering.” |
| Silicon |
Si |
2.32 |
1410 |
– |
0.712 |
992 |
1147 |
1337 |
Fair |
“Fabmate®‡, Tantalum” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Alloys with W; use heavy W boat. SiO produced.” |
| Silicon (II) Oxide |
SiO |
2.13 |
>1702 |
S |
0.87 |
– |
– |
850 |
Fair |
“Fabmate®, Tungsten, Tantalum” |
Ta |
W |
W |
Ta |
“RF, RF-R” |
“For resistance evaporation, use baffle box and low rate.” |
| Silicon (IV) Oxide |
SiO2 |
~2.65 |
1610 |
– |
**1.00 |
* |
* |
1025* |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite, Tantalum” |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
“Quartz excellent in E-beam.” |
| Silicon (N-type) |
“Si (N-type)” |
2.32 |
1410 |
– |
0.712 |
992 |
1147 |
1337 |
Fair |
“Fabmate®‡, Tantalum” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“DC, RF” |
– |
| Silicon (P-type) |
“Si (P-type)” |
2.32 |
1410 |
– |
0.712 |
992 |
1147 |
1337 |
Fair |
“Fabmate®‡, Tantalum” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“DC, RF” |
– |
| Silicon Boride |
SiB6 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Silicon Carbide |
SiC |
3.22 |
≈2700 |
“S, D” |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
1 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Sputtering preferred.” |
| Silicon Nitride |
Si3N4 |
3.44 |
1900 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈800 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Silicon Selenide |
SiSe |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Silicon Sulfide |
SiS |
1.85 |
940 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
450 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Silicon Telluride |
SiTe2 |
4.39 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Silver |
Ag |
10.5 |
962 |
– |
0.529 |
847 |
958 |
1105 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Tungsten, Molybdenum, Tantalum” |
W |
Mo |
“Ta, Mo” |
“Al2O3, W” |
DC |
– |
| Silver Bromide |
AgBr |
6.47 |
432 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
≈380 |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Silver Chloride |
AgCl |
5.56 |
455 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈520 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
Mo |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Silver Iodide |
AgI |
6.01 |
558 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Sodium |
Na |
0.97 |
98 |
– |
– |
74 |
124 |
192 |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
Q |
– |
“Preheat gently to outgas. Metal reacts quickly in air.” |
| Sodium Bromide |
NaBr |
3.2 |
747 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Sodium Chloride |
NaCl |
2.17 |
801 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
530 |
Good |
– |
“Ta, W, Mo” |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
“Copper oven; little decomposition. Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Sodium Cyanide |
NaCN |
– |
564 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Sodium Fluoride |
NaF |
2.56 |
993 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1000 |
Good |
“Tungsten, Fabmate®” |
“Mo, Ta, W” |
– |
– |
BeO |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas. No decomposition.” |
| Sodium Hydroxide |
NaOH |
2.13 |
318 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈470 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Spinel |
MgAI2O4 |
8 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Strontium |
Sr |
2.6 |
769 |
– |
**1.00 |
239 |
309 |
403 |
Poor |
– |
“W, Ta, Mo” |
W |
W |
VitC |
RF |
“Wets but does not alloy with W/Ta/Mo. May react in air.” |
| Strontium Chloride |
SrCl2 |
3.05 |
875 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Strontium Fluoride |
SrF2 |
4.24 |
1473 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈1000 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
– |
| Strontium Oxide |
SrO |
4.7 |
2430 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
1500 |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
“Reacts with W/Mo.” |
| Strontium Sulfide |
SrS |
3.7 |
>2000 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Strontium Titanate |
SrTiO3 |
– |
– |
– |
0.31 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Sulfur |
S |
2.07 |
113 |
– |
– |
13 |
19 |
57 |
Poor |
– |
W |
– |
W |
Q |
– |
“Bad for vacuum systems.” |
| Supermalloy® † |
Ni/Fe/Mo |
8.9 |
1410 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
Fabmate®‡, |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Sputtering preferred; or co-evaporate from 2 sources-Ni/Fe and Mo.” |
| T |
| Tantalum |
Ta |
16.6 |
2996 |
– |
0.262 |
1960 |
2240 |
2590 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Forms good films.” |
| Tantalum Boride |
TaB2 |
11.15 |
>3000 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Tantalum Carbide |
TaC |
13.9 |
3880 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈2500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Tantalum Nitride |
TaN |
16.3 |
3360 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Evaporate Ta in 10-3 Torr N2.” |
| Tantalum Pentoxide |
Ta2O5 |
8.2 |
1872 |
– |
0.3 |
1550 |
1780 |
1920 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Tantalum” |
Ta |
W |
W |
VitC |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Slight decomposition. Evaporate Ta in 10-3 Torr O2.” |
| Tantalum Sulfide |
TaS2 |
– |
>1300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Technetium |
Tc |
11.5 |
2200 |
– |
– |
1570 |
1800 |
2090 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Tellurium |
Te |
6.25 |
449 |
– |
0.9 |
157 |
207 |
277 |
Poor |
Fabmate® |
“W, Ta” |
W |
“W, Ta” |
“Al2O3, Q” |
RF |
“Wets without alloying.” |
| Terbium |
Tb |
8.23 |
1356 |
– |
0.66 |
800 |
950 |
1150 |
Excellent |
“Graphite, Fabmate®, Tantalum” |
Ta |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
RF |
– |
| Terbium Fluoride |
TbF3 |
– |
1172 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈800 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Terbium Oxide |
Tb2O3 |
7.87 |
2387 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Partially decomposes.” |
| Terbium Peroxide |
Tb4O7 |
– |
– |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Films TbO. |
| Thallium |
Tl |
11.85 |
304 |
– |
– |
280 |
360 |
470 |
Poor |
Fabmate® |
“W, Ta” |
– |
W |
“Al2O3, Q” |
DC |
Wets freely. |
| Thallium Bromide |
TlBr |
7.56 |
480 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈250 |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Thallium Chloride |
TlCl |
7 |
430 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈150 |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Thallium Iodide |
TlI |
7.1 |
440 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈250 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Thallium Oxide |
Tl2O2 |
10.19 |
717 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
350 |
<-/td> |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Disproportionates at 850°C to Tl2O.” |
| Thorium |
Th |
11.7 |
1.75 |
– |
– |
1430 |
1660 |
1925 |
Excellent |
“Molybdenum, Tantalum, Tungsten” |
“W, Ta, Mo” |
W |
W |
– |
– |
– |
| Thorium Bromide |
ThBr4 |
5.67 |
610 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Thorium Carbide |
ThC2 |
8.96 |
2655 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈2300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
C |
RF |
– |
| Thorium Fluoride |
ThF4 |
6.32 |
>900 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈750 |
Fair |
– |
Mo |
– |
W |
VitC |
RF |
– |
| Thorium Oxide |
ThO2 |
9.86 |
3220 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈2100 |
Good |
Tungsten |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Thorium Oxyfluoride |
ThOF2 |
9.1 |
900 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Mo, Ta” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Thorium Sulfide |
ThS2 |
7.3 |
1925 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Sputtering preferred; or co-evaporate from 2 sources.” |
| Thulium |
Tm |
9.32 |
1545 |
S |
– |
461 |
554 |
680 |
Good |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
Al2O3 |
DC |
– |
| Thulium Oxide |
Tm2O3 |
8.9 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Tin |
Sn |
7.28 |
232 |
– |
0.724 |
682 |
807 |
997 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Tantalum” |
Mo |
W |
W |
Al2O3 |
DC |
“Wets Mo low sputter power. Use Ta liner in E-beam guns. Low Melting Point materials not ideal for sputtering.” |
| Tin Oxide |
SnO2 |
6.95 |
1630 |
S |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1000 |
Excellent |
– |
W |
W |
W |
“Q, Al2O3” |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Films from W are oxygen deficient; oxidize in air.” |
| Tin Selenide |
SnSe |
6.18 |
861 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈400 |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Tin Sulfide |
SnS |
5.22 |
882 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈450 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Tin Telluride |
SnTe |
6.48 |
780 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
≈450 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Titanium |
Ti |
4.5 |
1660 |
– |
0.628 |
1067 |
1235 |
1453 |
Excellent |
Fabmate® |
W |
– |
– |
TiC |
DC |
“Alloys with W/Ta/Mo; evolves gas on first heating.” |
| Titanium (II) Oxide |
TiO |
4.93 |
1750 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1500 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Tantalum” |
“W, Mo” |
– |
– |
VitC |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Titanium (III) Oxide |
Ti2O3 |
4.6 |
2130 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Tantalum” |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Titanium (IV) Oxide |
TiO2 |
4.26 |
1830 |
– |
0.4 |
– |
– |
≈1300 |
Fair |
“Fabmate®, Tantalum” |
“W, Mo” |
– |
W |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Suboxide, must be reoxidized to rutile. Ta reduces TiO2 to TiO and Ti.” |
| Titanium Boride |
TiB2 |
4.5 |
2900 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Titanium Carbide |
TiC |
4.93 |
3140 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈2300 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Titanium Nitride |
TiN |
5.22 |
2930 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
Molybdenum |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Sputtering preferred. Decomposes with thermal evaporation.” |
| Tungsten |
W |
19.35 |
3410 |
– |
0.163 |
2117 |
2407 |
2757 |
Good |
“Direct in Hearth” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Forms volatile oxides. Films hard and adherent.” |
| Tungsten Boride |
WB2 |
10.77 |
≈2900 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Poor |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Tungsten Carbide |
WC |
17.15 |
2860 |
– |
0.151 |
1480 |
1720 |
2120 |
Excellent |
“Graphite, Fabmate®” |
C |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Tungsten Disulfide |
WS2 |
7.5 |
1250 |
D |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Tungsten Oxide |
WO3 |
7.16 |
1473 |
S |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
980 |
Good |
Tungsten |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF-R |
“Preheat gently to outgas. W reduces oxide slightly.” |
| Tungsten Selenide |
WSe2 |
9 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Tungsten Silicide |
WSi2 |
9.4 |
>900 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Tungsten Telluride |
WTe2 |
9.49 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| U |
| Uranium |
U |
19.05 |
1132 |
– |
– |
1132 |
1327 |
1582 |
Good |
– |
“Mo, W” |
W |
W |
– |
– |
Films oxidize. |
| Uranium (II) Sulfide |
US |
10.87 |
>2000 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Uranium (III) Oxide |
U2O3 |
8.3 |
8.3 1300 |
D |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
W |
– |
RF-R |
“Disproportionates at 1,300°C to UO2.” |
| Uranium (IV) Oxide |
UO2 |
10.96 |
2878 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
W |
– |
RF |
“Ta causes decomposition.” |
| Uranium (IV) Sulfide |
US2 |
7.96 |
>1100 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Slight decomposition.” |
| Uranium Carbide |
UC2 |
11.28 |
2350 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
2100 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
C |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Uranium Fluoride |
UF4 |
6.7 |
960 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
300 |
– |
– |
Ni |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Uranium Phosphide |
UP2 |
8.57 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1200 |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| V |
| Vanadium |
V |
5.96 |
1890 |
– |
0.53 |
1162 |
1332 |
1547 |
Excellent |
Tungsten |
“W, Mo” |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Wets Mo. E-beam-evaporated films preferred.” |
| Vanadium (IV) Oxide |
VO2 |
4.34 |
1967 |
S |
– |
– |
– |
≈575 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Sputtering preferred.” |
| Vanadium (V) Oxide |
V2O5 |
3.36 |
690 |
D |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Vanadium Boride |
VB2 |
5.1 |
2400 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Vanadium Carbide |
VC |
5.77 |
2810 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1800 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Vanadium Nitride |
VN |
6.13 |
2320 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
– |
| Vanadium Silicide |
VSi2 |
4.42 |
1700 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Y |
| Ytterbium |
Yb |
6.96 |
819 |
S |
1.13 |
520 |
590 |
690 |
Good |
Tantalum |
Ta |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
| Ytterbium Fluoride |
YbF3 |
– |
1157 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈800 |
– |
“Tantalum, Molybdenum” |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Ytterbium Oxide |
Yb2O3 |
9.17 |
2346 |
S |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈1500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
Loses oxygen. |
| Yttrium |
Y |
4.47 |
1522 |
– |
0.835 |
830 |
973 |
1157 |
Excellent |
Tungsten |
“W, Ta” |
W |
W |
Al2O3 |
“RF, DC” |
“High Ta solubility.” |
| Yttrium Aluminum Oxide |
Y3Al5O12 |
– |
1990 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
W |
W |
– |
RF |
“Films not ferroelectric.” |
| Yttrium Fluoride |
YF3 |
4.01 |
1387 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“Tantalum, Molybdenum” |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Yttrium Oxide |
Y2O3 |
5.01 |
2410 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈2000 |
Good |
“Fabmate®, Graphite, Tungsten” |
W |
– |
– |
C |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Loses oxygen; films smooth and clear.” |
| Z |
| Zinc |
Zn |
7.14 |
420 |
– |
0.514 |
127 |
177 |
250 |
Excellent |
“Fabmate®, Graphite, Tungsten” |
“Mo, W, Ta” |
W |
W |
“Al2O3, Q” |
DC |
“Evaporates well under wide range of conditions.” |
| Zinc Antimonide |
Zn3Sb2 |
6.33 |
570 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Zinc Bromide |
ZnBr2 |
4.2 |
394 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈300 |
– |
– |
W |
– |
– |
C |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Zinc Fluoride |
ZnF2 |
4.95 |
872 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
≈800 |
– |
– |
Ta |
– |
– |
Q |
RF |
– |
| Zinc Nitride |
Zn3N2 |
6.22 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Mo |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
Decomposes. |
| Zinc Oxide |
ZnO |
5.61 |
1975 |
– |
0.556 |
– |
– |
≈1800 |
Fair |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF-R |
– |
| Zinc Selenide |
ZnSe |
5.42 |
>1100 |
– |
0.722 |
– |
– |
660 |
– |
“Tantalum, Molybdenum” |
“Ta, W, Mo” |
“W, Mo” |
“W, Mo” |
Q |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas. Evaporates well.” |
| Zinc Sulfide |
ZnS |
3.98 |
1700 |
S |
0.775 |
– |
– |
≈800 |
Good |
“Tantalum, Molybdenum” |
“Ta, Mo” |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas. Films partially decompose. n=2.356.” |
| Zinc Telluride |
ZnTe |
6.34 |
1239 |
– |
0.77 |
– |
– |
~600 |
– |
– |
“Mo, Ta” |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
“Preheat gently to outgas.” |
| Zirconium |
Zr |
6.49 |
1852 |
– |
0.6 |
1477 |
1702 |
1987 |
Excellent |
– |
W |
– |
– |
– |
DC |
“Alloys with W. Films oxidize readily.” |
| Zirconium Boride |
ZrB2 |
6.09 |
≈3200 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Good |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Zirconium Carbide |
ZrC |
6.73 |
3540 |
– |
0.264 |
– |
– |
≈2500 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Zirconium Nitride |
ZrN |
7.09 |
2980 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Reactively evaporate in 10-3Torr N2.” |
| Zirconium Oxide |
ZrO2 |
5.89 |
≈2700 |
– |
**1.00 |
– |
– |
≈2200 |
Good |
“Graphite, Tungsten” |
W |
– |
– |
– |
“RF, RF-R” |
“Films oxygen deficient, clear and hard.” |
| Zirconium Silicate |
ZrSiO4 |
4.56 |
2550 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |
| Zirconium Silicide |
ZrSi2 |
4.88 |
1700 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
RF |
– |